Medical Device Cybersecurity: Meeting US/FDA Standards
In order to distribute medical devices in US, it is crucial for manufacturers to meet the established medical device cybersecurity requirements set out by the Food and Drugs Administration (FDA). This means that manufacturers must submit a premarket submission to the FDA to ensure that they are meeting the market access requirements.
FDA Premarket Requirements
These requirements include:
- Software Overview
A description of significant software features, functions, analyses, inputs, outputs, hardware platforms, and related diagrams or flows. - Development and Configuration Summary
A summary of the life cycle development plan, configuration management, and maintenance activities. - Cybersecurity Risk Assessment
A risk assessment that includes risk analysis, evaluation, control, and FDA-recommended SPDF usage for cybersecurity risks. - Software Update Protocols
Standard operating procedures for software updates, patch management, security assessments, and incident response plans. - Post-Market Surveillance Plan
A plan detailing methods for vulnerability monitoring, identification protocols, and response strategies. - Software Bill of Materials (SBOM)
A detailed SBOM listing all software components, including version numbers, licenses, and supplier information. - Cybersecurity Testing Evidence
Evidence that demonstrates cybersecurity testing has been conducted.
Applus+ Laboratories offers comprehensive cybersecurity testing services for evaluating medical devices in US / FDA Guidance on Cybersecurity in Medical Devices – Quality System Considerations and Content of Premarket Submissions.
Documentation Levels for Cybersecurity Testing and Device Risk Assessment
For the cybersecurity testing, and generally for all documentation required by the standard, two levels are defined in: Basic Documentation Level and Enhanced Documentation Level.
Here are a few examples of how the different levels are applied:
- A non-contact infrared thermometer intended for intermittent measurement of body temperature from the forehead not connected to other devices.
- Rationale: In general, a failure or latent flaw of the device software function(s) would not present a hazardous situation with a probable risk of death or serious injury to either a patient, user of the device, or others in the environment of use, prior to the implementation of risk control measures.
- Outcome: Basic Documentation Level.
- An implantable cardiac pacemaker used to treat bradycardia; the device is an implanted, programmable dual-chamber pulse generator with some Bluetooth capabilities.
- Rationale: A failure or latent flaw of the device software function(s), such as failure to pace or a latent flaw leading to incorrect sensing of an ectopic beat, would lead to a hazardous situation that would present a probable risk of death or serious injury to the patient prior to the implementation of risk control measures.
- Outcome: Enhanced Documentation Level.
- A non-patient-matched hip prosthesis that contains no firmware or other means for software-based control.
- Rationale: The device does not contain software.
- Outcome: No Documentation Level
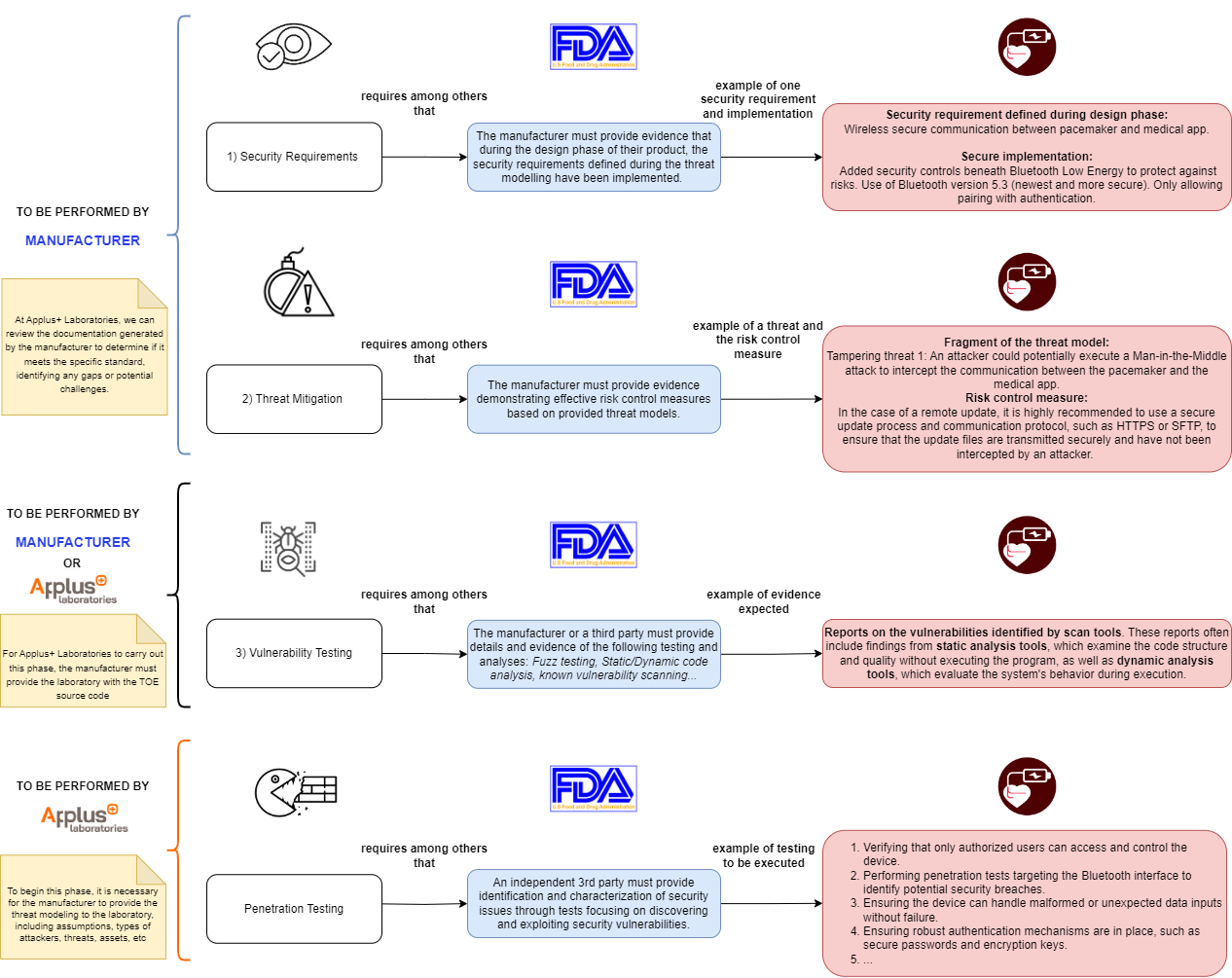
Medical Devices Documentation Procedure
Every medical device with a basic or higher documentation level must address a cybersecurity testing procedure. The evidence required to meet the cybersecurity testing standards is as follows (using the example of an implantable cardiac device with Bluetooth capabilities):
Contact Applus+ Laboratories to test and certify the cybersecurity of your medical devices!